Describe the Composition of Macromolecules Required by Living Organisms.
They are simply a catalyst of these. Describe the composition of macromolecules required by living organisms.
Describe the composition of macromolecules required by living organisms.

. Polysaccharides commonly known as carbohydrates are macromolecules. This is the currently selected item. Four types of macromolecules.
Contain N in rings nucleotides made of sugar phosphate and nitrogenous base. They are required for energy structure DNA enzymes etc. Macromolecules also function to produce the energy needed by cells for growth or reproduction.
When we consume food we intake the large biological molecules found in the food. Proteins carbohydrates nucleic acids and lipids are the four major classes of biological macromoleculeslarge molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules. 1- Describe the composition of macromolecules required by living organisms Practice and Skill Practice 2.
Explain how a change in the subunits of a polymer may lead to changes in structure or function of the macromolecule. Describe the properties of the monomers and the type of bonds that connect the monomers in biological macromolecules. Learning Objective Essential Knowledge ENE-1A Describe the composition of macromolecules required by living organisms.
Macromolecules are also termed as polymers. Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules. TEAS- Life and Physical Sciences- Basic Macromolecules in a Biological system.
Macromolecules required by living organisms. Contain N have N-C-C backbone. Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy starch and glycogen and ribose for our body.
They usually also contain hydrogen and oxygen as well as nitrogen and additional minor elements. OHs on all carbons except one. 13 Introduction to Biological Macromolecules.
Properties structure and function of biological macromolecules. Peptide bond is produced when carboxyl radical of one amino acid reacts with the amino -NH 2 group of the other amino acidThe basic structural formula of amino acids is. Proteins are large molecules consisting of many amino-acids connected by peptide linkages.
Made of CH and O. Macromolecules play a vital role in the survival of living things because they make up structures such as tissues and organs. The highly complex organization of living systems requires constant input of energy and the exchange of macromolecules.
Arrangement of atoms monomer combine by dehydration into macromolecules can function as food groups which are broken down by hydrolysis. Lots of C-H bonds. They are formed by the polymerisation of molecules such as carbon hydrogen and oxygen.
Macromolecules are made up of single units known as monomers that are joined by covalent bonds to form larger polymers. There are four major classes of biological macromolecules. In fact the basis for all biological macromolecules is long carbon chains with attached hydrogens.
Enzymes are the biological catalysts that decrease the amount of energy including heat that is needed for a chemical reaction and they also speed up the chemical reactions in the body but they themselves are not altered or changed as a result of this reaction. Such molecules can be termed as carbohydrates proteins lipids fats and nucleic acids. Get Quizlets official TEAS - 2005 terms 553 practice questions 2 full practice tests.
ENE-1A1 Organisms must exchange matter with the environment to grow reproduce and maintain organization. Describe the properties of the monomers and the type of bonds that connect the monomers in biological macromolecules. Overview of protein structure.
Made of CH and O. Hydrocarbons are naturally nonpolar and hydrophobic. Biological macromolecules all contain carbon in ring or chain form which means they are classified as organic molecules.
Start studying Unit 1 Review. They do not act as energy storage. In this post we will be discussing the structure of common biological macromolecules.
TOPIC 13 Introduction to Biological Macromolecules SYI-1B Describe the properties of the monomers and the type of bonds that connect the monomers in biological macromolecules. ENE-1A Describe the composition of macromolecules required by living organisms. Majority of living cells are rich in carbohydrates and they are the final products of many metabolic processes.
May have some CC bonds unsaturated Protein. Describe characteristics of a biological concept process or model represented visually. Organisms must exchange matter with the environment to grow reproduce and maintain organization ENE-1A Describe the composition of macromolecules required by living organisms.
We call these chains of carbon and hydrogen hydrocarbons. Molecular structure of triglycerides fats Saturated fats unsaturated fats and trans fats. However by adding different atoms and functional groups to a carbon chain it can take on a wide variety of other properties.
14 Properties of Biological Macromolecules. Enzymes are hydrophilic globular protein macromolecules. They are made up of monosaccharides sugar molecules.
In this article we will discuss about the composition and structure of proteins. Atoms and molecules from the environment are necessary to build new molecules Carbon moves from the environment to organisms where it is. The monomer units of macromolecules are polar in nature with their heads and tails with different physical and chemical properties.
Describe the composition of macromolecules required by living organisms. Explain how a change in the subunits of a polymer may lead to changes in structure or function of the macromolecule. Carbohydrates lipids proteins nucleic acids.
Analyze Visual Representations of Biological Concepts and Processes. Describe the properties of the monomers and the type of bonds that connect the monomers in biological macromolecules. Macromolecules are so huge that these are made up of more than 10000 or more atoms.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.

Significance Of Aesthetics In Art Learn About Arts Education Art Education Education Infographic

How Phospholipids Help Hold A Cell Together Biochemistry Biochemistry Notes Teaching Biology

Cmap Of Biological Compounds Biology Organic Molecules Worksheets Free
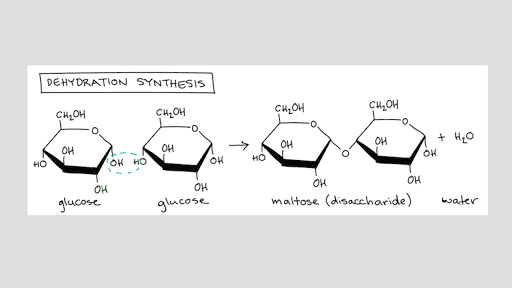
Introduction To Macromolecules Article Khan Academy

This Image Demonstrates The Idea Of Anatomical Variation No Two Humans Have The Same Anatomy We Are Not All Textbo Anatomy And Physiology Physiology Textbook

Ap Biology Unit 6 Lesson Note Taker And Review Bundle No Prep Video Video High School Science Activities Lesson Unique Teaching Resources

Macromolecule Definition Examples Britannica

Proteins Paul Anderson Of Bozeman Science Explains The Structure And Importanc Kindergarten Worksheets Sight Words Science Worksheets Social Studies Worksheets

Monatomic Gases Have The Smallest Specific Heat Cv Molecules Macromolecules Molecular Mass

Active Reading Bundle Cells And Organelles Textbook Series Ch2 W Pdf Form Reading Bundle Cell Theory Chemistry Lessons

Bacterial Metabolite Production Biology Microbiology Secondary

Properties Of Polymers Boundless Chemistry

This Flow Chart Shows The Steps In Digestion Of Carbohydrates The Different Levels Shown Are Starch Carbohydrates Biology Biology Notes Anatomy And Physiology

Create A Concept Map Of Biomolecules Concept Map Biology Activity Graphic Organizers

Meiosis Spermatogenesis Oogenesis Medical Knowledge Meiosis Chemistry Help

Ncert Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Mass Percentage Composition 11th Chemistry Chemistry Solutions

A Level Biology Factors Affecting Enzymes Revision A Level Biology Biology Notes Biology



Comments
Post a Comment